A Beginner’s Guide to Heat Exchangers
A Beginner’s Guide to Heat Exchangers
A Beginner’s Guide to Heat Exchangers : Heat exchangers are gadgets that transfer heat from one fluid (liquid or gas) to another without mixing them. They play a vital part in a assortment of applications, from power generation and industrial forms to heating and cooling frameworks in homes and cars. Understanding how heat exchangers work and where they are utilized can help you appreciate their importance in everyday life.
What is a Heat Exchanger?
A heat exchanger is basically a system outlined to transfer heat between two or more liquids, which can either be gases, fluids, or a combination of both. The liquids are isolated by a solid boundary, usually made of metal, which permits warm to pass through but anticipates the fluids from mixing. Heat exchangers are productive, dependable, and basic for maintaining temperature control in numerous systems.
How Do Heat Exchangers Work?
Heat exchangers work on the guideline of thermal energy transfer. When two liquids at different temperatures come into nearness, heat normally flows from the hotter liquid to the cooler one. The heat exchanger encourages this handle by giving a surface range where the heat exchange can take put. The bigger the surface range and the greater the temperature difference between the liquids, the more effective the heat transfer.
There are a few ways that heat exchangers can be outlined to optimize this heat transfer:
Parallel Stream: Both liquids move within the same direction through the exchanger.
Counterflow: The liquids flow in inverse directions, maximizing heat transfer proficiency.
Crossflow: The fluids move opposite to each other, a plan commonly used in air conditioning systems.
Types of Heat Exchangers
There are a few sorts of heat exchangers, each suited to different applications:
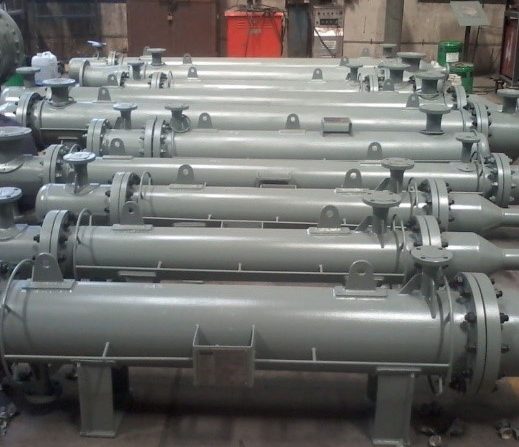
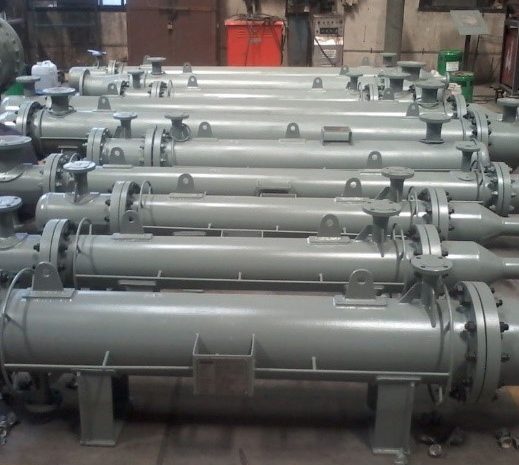
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: One of the foremost common sorts, it comprises of a series of tubes inside a cylindrical shell. One liquid streams through the tubes, whereas the other flows around the tubes inside the shell. This plan is broadly used in control plants, refineries, and chemical forms due to its strength and productivity.
Plate Heat Exchanger: Made up of lean, corrugated plates stacked together, this sort permits the liquids to flow between the plates. Plate heat exchangers offer a tall surface region for heat exchange in a compact plan, making them perfect for HVAC systems, nourishment handling, and refrigeration.
Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger: Rather than utilizing water or another fluid to cool the hot liquid, this exchanger uses air. Common in car radiators and a few industrial processes, air-cooled heat exchangers are especially useful where water is scarce or expensive.
Double Pipe Heat Exchanger: This straightforward design highlights one pipe interior another, with one liquid flowing through the internal pipe and the other liquid streaming within the inverse course within the outer pipe. It’s frequently utilized in littler applications where less heat transfer is required.
Applications of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are everywhere. In homes, they’re found in heating and cooling systems, making a difference to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. In vehicles, they cool engines and provide air conditioning. Industrially, they are essential in forms like chemical fabricating, oil refining, and power generation, where they oversee temperature and improve energy productivity.
Conclusion
Heat exchangers are vital components in numerous of the systems we depend on every day. By efficiently transferring heat between liquids, they offer assistance to save energy, diminish costs, and maintain the usefulness of different forms. Whether in huge industrial plants or little household appliances, the part of heat exchangers is essential in making our modern world work easily. Understanding the essentials of how they work and where they’re utilized can donate you a greater appreciation for these irreplaceable devices.