Air Cooled Heat Exchangers and Their Industrial Applications
Introduction
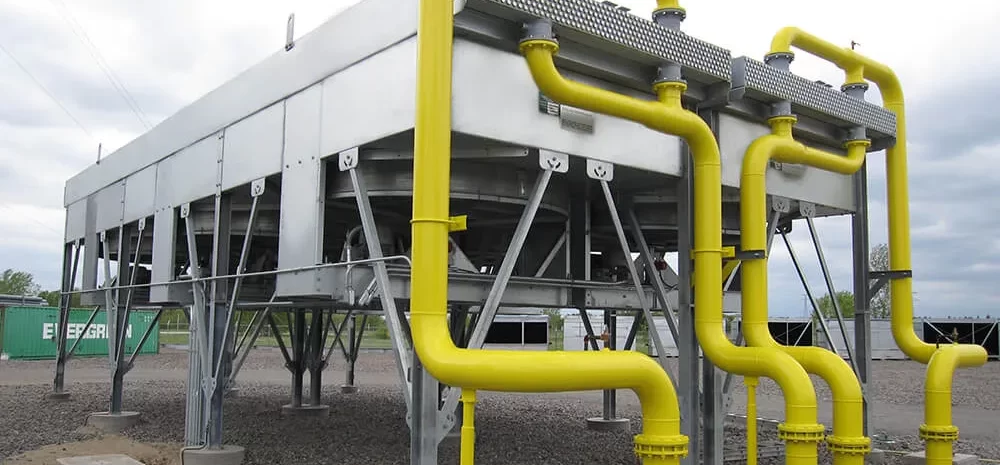
Air-cooled heat exchangers (ACHEs) AIR COOLED HEAT EXCHANGERare essential in industries where water scarcity or environmental regulations restrict the use of water-cooled systems. These exchangers transfer heat from fluids (such as water, oil, or refrigerants) to the surrounding air. Here’s a detailed look at the main types of air-cooled heat exchangers and their industrial applications
Types of Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Forced Draft Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
In forced draft ACHEs, fans are placed at the front (inlet) of the heat exchanger, blowing air through the cooling fins. These systems typically operate with lower fan power requirements and are preferred in applications where space is limited. Key advantages include:
- Lower initial cost: Due to simpler design and reduced material requirements.
- Flexibility: Suitable for a variety of configurations and can be installed in confined spaces.
- Applications: Commonly used in power plants, oil refineries, and compressor stations.
Induced Draft Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
In induced draft systems, fans are located at the rear (outlet) of the heat exchanger, pulling air through the cooling fins. These systems generally provide more uniform air distribution and better heat rejection efficiency. Key advantages include:
- Better temperature control: Ideal for applications requiring precise cooling.
- Reduced noise: Fans are placed downstream, resulting in lower noise levels.
- Applications: Widely used in chemical processing plants, natural gas processing units, and large-scale refrigeration systems.
Natural Draft Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Natural draft ACHEs rely on natural convection rather than mechanical fans to move air through the exchanger. This design is suitable for low-energy or remote applications where access to electricity is limited or energy efficiency is a priority. Key advantages include:
- No power consumption: Completely passive system, reducing operational costs.
- Minimal maintenance: With no moving parts, these exchangers have a long service life.
- Applications: Often found in renewable energy plants, small-scale industrial processes, and isolated facilities.
Hybrid Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Hybrid ACHEs combine air and water cooling, utilizing both air and a water spray system to increase cooling capacity during peak loads. These systems are effective in areas with fluctuating environmental conditions. Key advantages include:
- Increased efficiency: Can handle higher heat loads by using water when air cooling alone is insufficient.
- Flexibility: Can be operated as a dry cooler when water use is restricted.
- Applications: Used in power generation, petrochemical refineries, and data centers requiring high cooling loads.
Industrial Applications of Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Oil & Gas Industry
Air-cooled heat exchangers are widely used in upstream, midstream, and downstream oil and gas operations. They cool process fluids, such as oil, gas, and condensates, in refineries, gas processing plants, and pipelines. Forced and induced draft systems are commonly used here for their ability to handle large volumes of heat in high-temperature environments.
Power Generation
In power plants, ACHEs are crucial for cooling turbine condensers, generator systems, and auxiliary equipment. They help maintain operational efficiency while reducing water consumption. Natural draft exchangers can be found in renewable energy plants, like wind farms and solar power stations, to cool electrical components.
Chemical and Petrochemical Industry
Chemical plants and petrochemical refineries use air-cooled heat exchanger to cool reactors, condensers, and distillation units. Induced draft systems are particularly effective in this sector, as they provide precise temperature control required for sensitive chemical reactions.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage sector, ACHEs are employed in refrigeration, fermentation, and cooling of process fluids. They are crucial in maintaining temperature consistency during production, ensuring product quality and safety. Hybrid systems are sometimes used to handle high cooling demands in this industry.
HVAC and Refrigeration
Air-cooled heat exchanger are integral components in HVAC systems, providing cooling for commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and residential complexes. They also play a key role in industrial refrigeration applications, such as cold storage, dairy processing, and pharmaceutical production.
Renewable Energy Sector
In renewable energy applications, such as geothermal plants, biomass facilities, and solar thermal power stations, air-cooled heat exchanger are used to manage heat rejection. Natural draft exchangers, in particular, are preferred for their low environmental impact and energy efficiency.
Mining and Metallurgy
The mining and metallurgy industries utilize air-cooled heat exchangers to cool equipment, such as crushers, grinding mills, and conveyor systems. Forced draft exchangers are commonly used here due to their ability to handle harsh operating conditions, such as high dust and temperature environments.
Conclusion
Air-cooled heat exchanger offer a reliable and environmentally friendly cooling solution for a wide range of industries. By understanding the different types of ACHEs and their specific applications, industries can select the most suitable system for their cooling needs, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.