Antifreeze in Chiller Systems
Introduction
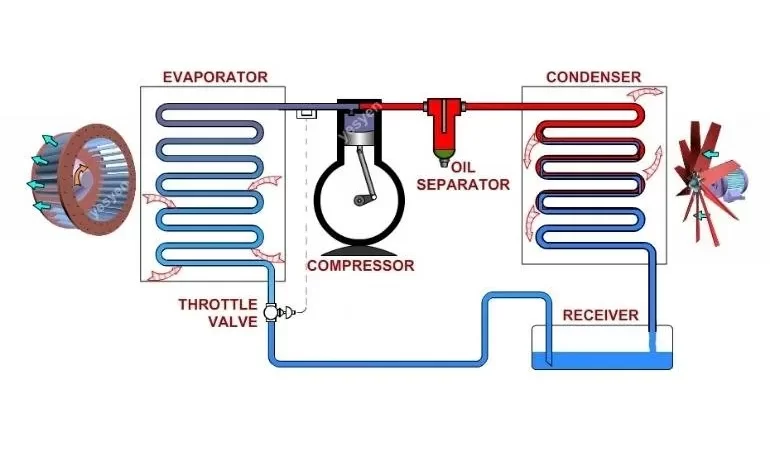
Antifreeze in Chiller Systems plays a crucial role in chiller systems, especially in climates where temperatures can fall below freezing. In these systems, antifreeze prevents the liquid within the chiller from freezing, which could lead to pipe bursts, extensive system damage, and costly repairs. By lowering the freezing point of the coolant, antifreeze ensures the smooth operation of chillers in cold environments. However, selecting the right antifreeze involves balancing factors like toxicity, thermal performance, compatibility with chiller materials, and environmental impact. Using the correct formulation not only protects the system but also enhances efficiency and extends the chiller’s operational life.
Types of Antifreeze for Chiller Systems
Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol is a popular choice due to its excellent heat transfer capabilities and effectiveness in preventing freezing. However, it is toxic and should be used with caution in applications where human contact is possible, such as food processing or pharmaceuticals.
Propylene Glycol
Propylene glycol is less toxic and safer for applications where human exposure might occur. It is commonly used in food and beverage processing industries, as well as in pharmaceutical chillers, due to its low health risk profile.
Methanol
Methanol is an alternative antifreeze, but it’s typically used only in specific industrial applications where the risks of handling this highly flammable and toxic chemical can be controlled.
Hybrid Glycol Formulations
Combining different glycols can optimize performance, balancing toxicity, thermal efficiency, and cost. These formulations can be tailored to specific application needs.
Choosing the Right Formulation
When choosing an antifreeze for chiller systems, it’s essential to balance the toxicity, thermal performance, and cost of the formulation:
- Application Requirements: Select based on the environment and any health or safety regulations, such as using propylene glycol for food and beverage applications.
- Temperature Conditions: Ensure that the antifreeze can handle the lowest temperature expected in the application.
- System Compatibility: Verify compatibility with the materials used in the chiller, as some formulations may cause corrosion or react with system components.
Concentration and Mixture Ratios
The concentration of antifreeze should be carefully managed to achieve optimal freezing protection without overly affecting heat transfer efficiency. Too high a concentration can reduce thermal performance, while too low a concentration may not provide adequate freeze protection.
Environmental Considerations
- Biodegradability: Some antifreeze formulations are more environmentally friendly than others. Propylene glycol, for example, is less harmful to the environment compared to ethylene glycol.
- Spill Management: Implement protocols for handling and disposing of antifreeze to minimize environmental impact in case of spills or leaks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the chosen antifreeze meets environmental regulations and standards relevant to your region and industry.
Cost Implications
- Initial Cost: Different antifreeze formulations come with varying price points. Balancing upfront costs with long-term benefits is crucial.
- Maintenance Costs: Consider the frequency of maintenance required for different antifreeze types, including potential costs for additives or inhibitors.
- System Efficiency: Higher-quality antifreeze formulations may improve system efficiency, potentially lowering energy costs over time.
Maintenance Practices
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor antifreeze levels and concentration to ensure optimal performance.
- Periodic Testing: Conduct regular tests for pH levels, corrosion inhibitors, and overall fluid quality.
- System Flushing: Periodically flush the chiller system to remove old antifreeze and contaminants, replacing it with fresh formulation as needed.
Conclusion
Selecting the right antifreeze formulation for chiller systems involves a comprehensive evaluation of various factors, including toxicity, thermal performance, cost, environmental impact, and system compatibility. By carefully considering these aspects and staying informed about industry best practices and emerging technologies, you can ensure the reliable and efficient operation of your chiller systems, even in challenging temperature conditions.