Components of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Components of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
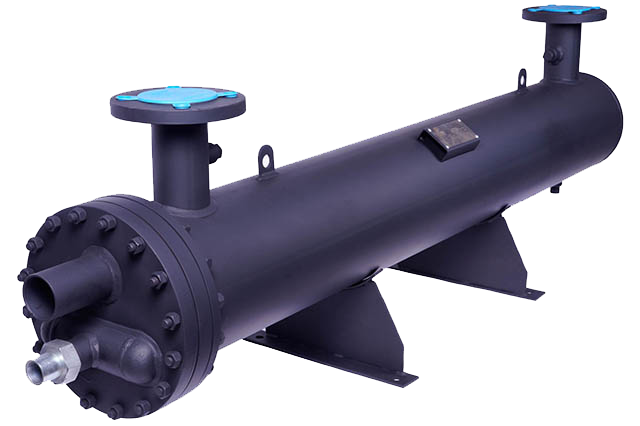
Shell and tube heat exchangers are complicated systems composed of a few key components of shell and tube heat exchanger, each playing a imperative part within the exchange of heat between fluids. At the heart of these exchangers lies the shell, a vigorous outer vessel that houses the inside components. Inside this shell are various tubes, slim conduits through which fluids circulate. Tube sheets, situated at both closes of the shell, secure the tubes in put and make a seal to prevent leakage.
Baffles, strategically put interior the shell, direct fluid flow to optimize heat exchange productivity. These baffles coordinate the flow of liquids over the tube bundle, upgrading mixing and turbulence for improved thermal execution. The tube bundle itself comprises the organize of tubes encased inside the shell, shaping the essential interface for heat exchange.
To get to the tube bundle for maintenance and inspection, a bonnet or channel cover is introduced at one end of the shell. This detachable cover permits specialists to benefit the heat exchanger without compromising its judgment. Furthermore, development joints are consolidated to accommodate thermal development and contraction of the tubes during operation, guaranteeing structural integrity and life span.
Pass partitions advance segment the shell into particular areas, making parallel flow ways for liquids and optimizing heat transfer proficiency. These segments advance uniform liquid distribution and avoid blending between the channel and outlet streams. Nozzles, deliberately situated on the shell, serve as entry and exit points for fluids, encouraging consistent flow inside the exchanger.
Lastly, robust back structures guarantee stability and arrangement of the heat exchanger inside the system. These supports protect against vibration and mechanical push, protecting the integrity and performance of the shell and tube heat exchanger.
In summary, the intricate plan and integration of these components enable shell and tube heat exchangers to productively transfer heat between fluids, making them indispensable devices in a wide run of industrial applications.