Green Hydrogen Energy
Introduction
Green hydrogen energy is rapidly emerging as a game-changing solution in the global shift towards sustainable and clean energy systems. Unlike conventional hydrogen production methods that rely on fossil fuels, green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower, making it a zero-emission fuel. This technology offers a significant opportunity to reduce carbon footprints, enhance energy security, and create a more sustainable future by replacing traditional fossil fuels in industries, transportation, and power generation. As the world faces climate change challenges, energy crises, and growing environmental concerns, governments and industries are actively investing in hydrogen infrastructure and technology. With increasing advancements in electrolysis efficiency, storage solutions, and cost reduction strategies, green hydrogen is poised to become a key pillar of the future energy landscape. The ability to store and transport clean energy over long distances further enhances its potential as a global energy carrier, making it a viable alternative to conventional fuels.
Production of Green Hydrogen
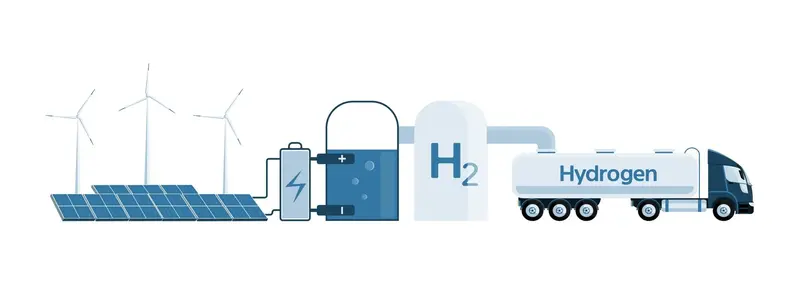
Green hydrogen is primarily produced using the electrolysis process, which involves splitting water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using electricity generated from renewable sources. The steps involved in producing green hydrogen include:
-
Electricity Generation – Renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or hydropower plants generate electricity.
-
Electrolysis Process – The electricity is used to power an electrolyzer, which splits water into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂).
-
Hydrogen Collection – The hydrogen gas is separated and collected for storage and distribution.
-
Storage & Transportation – Hydrogen is stored as a compressed gas, liquid, or within chemical carriers for further use.
-
Utilization – The stored hydrogen is used in fuel cells, power plants, industrial applications, and transportation.
Types of Hydrogen Based on Production
Hydrogen is classified into different types based on how it is produced:
-
Green Hydrogen – Produced through electrolysis using renewable energy, resulting in zero emissions.
-
Blue Hydrogen – Produced from natural gas with carbon capture and storage (CCS) to reduce emissions.
-
Grey Hydrogen – Produced from natural gas without carbon capture, resulting in high CO₂ emissions.
-
Brown Hydrogen – Derived from coal gasification, releasing significant amounts of carbon emissions.
-
Pink Hydrogen – Produced using nuclear energy to power electrolysis.
Applications of Green Hydrogen
Green hydrogen has a wide range of applications across various industries, helping reduce carbon footprints and providing clean energy solutions.
-
Power Generation
-
Used in fuel cells to generate electricity with zero emissions.
-
Can be combined with renewable energy sources to create hybrid energy systems.
-
Provides a backup power supply to stabilize energy grids.
-
-
Industrial Use
-
Used in steel production to replace coal, reducing carbon emissions.
-
Supports the production of ammonia, fertilizers, and chemicals.
-
Used in oil refining for desulfurization processes.
-
-
Transportation
-
Used in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs), including cars, buses, trucks, and trains.
-
Provides longer range and faster refueling than battery-electric vehicles.
-
Supports the decarbonization of heavy-duty transport and aviation.
-
-
Residential & Commercial Heating
-
Can be blended with natural gas for domestic heating.
-
Used in hydrogen boilers and fuel cells for efficient heating solutions.
-
-
Aerospace & Space Exploration
-
Used as rocket fuel due to its high energy density.
-
Powers space missions and satellites with clean and efficient propulsion systems.
-
Advantages of Green Hydrogen
Green hydrogen provides numerous benefits, making it a viable solution for the future of clean energy.
-
Zero Carbon Emissions – 100% clean and environmentally friendly.
-
Sustainable & Renewable – Uses energy from solar, wind, and hydropower.
-
Efficient Energy Storage – Stores excess renewable energy for long durations.
-
Versatile Applications – Used in power generation, industry, transport, and heating.
-
Reduces Dependence on Fossil Fuels – Provides a clean alternative to coal, oil, and gas.
-
Improves Energy Security – Reduces reliance on imported energy sources.
-
Supports Grid Balancing – Helps stabilize electric grids by storing surplus energy.
-
High Energy Density – More energy-efficient than fossil fuels.
Challenges & Limitations
Despite its advantages, green hydrogen faces some technical and economic challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption.
-
High Production Costs – Electrolysis remains expensive compared to traditional hydrogen production.
-
Infrastructure Development – Requires investments in storage, transportation, and refueling stations.
-
Water Consumption – Electrolysis requires large amounts of water, which may be an issue in water-scarce regions.
-
Energy Intensive – The process requires large amounts of electricity, making it dependent on renewable energy availability.
-
Storage and Distribution Challenges – Hydrogen has low energy density and requires specialized storage solutions.
Future of Green Hydrogen
The global push towards clean energy and carbon neutrality is accelerating the development of green hydrogen technology. Key trends shaping the future include:
-
Cost Reduction – Advancements in electrolysis technology and economies of scale will make green hydrogen more affordable.
-
Government Policies & Incentives – Many countries are introducing subsidies, tax benefits, and hydrogen strategies to promote adoption.
-
Hydrogen Infrastructure Expansion – Increased investment in hydrogen refueling stations, pipelines, and storage facilities.
-
Integration with Renewables – Green hydrogen will play a major role in balancing solar and wind energy fluctuations.
-
Adoption in Heavy Industries – More industries will shift towards hydrogen-based manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
Green hydrogen energy is more than just a renewable energy source—it is a revolutionary solution that can drive the world towards a sustainable, low-carbon future. By leveraging renewable energy sources for hydrogen production, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance energy security, and transition away from fossil fuel dependency. Although there are challenges such as high production costs, infrastructure limitations, and energy requirements, continuous innovation, policy support, and large-scale investment are driving rapid advancements in hydrogen technology. The global push towards net-zero emissions and green energy adoption will accelerate the integration of green hydrogen into various sectors, making it a cornerstone of future energy systems. With its ability to store excess renewable energy, power industries, and fuel clean transportation, green hydrogen is set to revolutionize the way we produce, store, and consume energy.