How Heat Exchangers Power Our World
How Heat Exchangers Power Our World
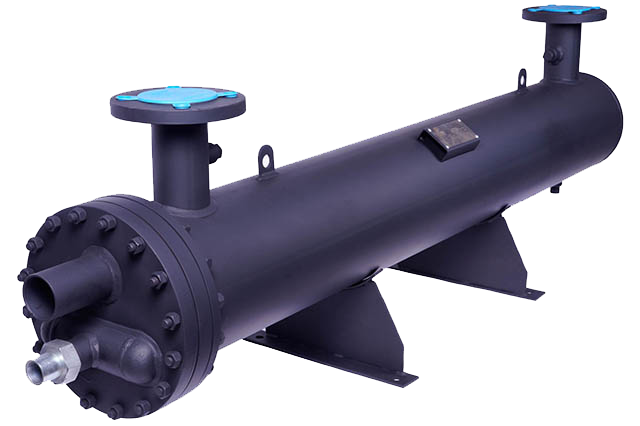
How Heat Exchangers Power Our World : Heat exchangers are an indispensably part of numerous systems that control our world, from electricity generation to industrial forms and indeed the heating and cooling of our homes. These gadgets, which transfer heat between two or more liquids, empower proficient energy utilize, improve prepare effectiveness, and contribute to environmental supportability. Here’s a see at how heat exchangers play a crucial part in powering our world:
1. Electricity Generation
1.1 Power Plants
Steam Power Plants: In steam power plants, heat exchangers are utilized to transfer heat from the combustion of fossil fills to water, creating steam that drives turbines to create electricity. The steam is at that point condensed back into water employing a condenser, another type of heat exchanger, and recirculated within the system.
Atomic Power Plants: In atomic control plants, heat exchangers transfer warm from the atomic reactor center to a auxiliary circle, creating steam that drives turbines. This handle isolates the radioactive fabric from the rest of the plant, guaranteeing safety.
1.2 Renewable Vitality
Solar Thermal Power: Heat exchangers in solar thermal power plants capture heat from concentrated solar control (CSP) systems and exchange it to a working liquid, which generates steam to drive turbines.
Geothermal Power: In geothermal power plants, heat exchangers exchange heat from underground hot water or steam to a auxiliary liquid, which at that point drives a turbine to deliver electricity.
2. Mechanical Forms
2.1 Chemical and Petrochemical Businesses
Chemical Reactors: Heat exchangers are fundamental in controlling the temperature of chemical responses, ensuring ideal response rates and item quality. They either expel excess heat from exothermic responses or supply heat to endothermic forms.
Refineries: In oil refineries, heat exchangers are utilized in forms like refining, where they preheat the unrefined oil before it enters the refining column, progressing proficiency and reducing energy utilization.
2.2 Food and Refreshment Industry
Pasteurization: Heat exchangers are utilized in pasteurization forms to heat fluids, such as milk or juice, to a specific temperature to kill harmful microorganisms and then quickly cool them down to protect quality.
Refrigeration and Cooling: In nourishment processing, heat exchangers cool items quickly to extend rack life, maintain safety measures, and move forward item quality.
3. HVAC Systems (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
3.1 Residential and Commercial Buildings
Heating Systems: In HVAC systems, heat exchangers transfer heat from boilers or heaters to air or water, which is at that point distributed all through buildings to preserve comfortable indoor temperatures.
Air Conditioning: Heat exchangers in air conditioning systems retain heat from indoor air and transfer it exterior, cooling the air interior homes and commercial spaces.
3.2 Area Heating and Cooling
Centralized Systems: In locale heating and cooling systems, centralized warm exchangers disseminate thermal energy to different buildings from a single source, such as a power plant or geothermal well, improving energy productivity and diminishing carbon outflows.
4. Transportation
4.1 Automotive Applications
Engine Cooling: In vehicles, heat exchangers, commonly known as radiators, cool the motor by transferring heat from the motor coolant to the air, avoiding overheating and guaranteeing ideal execution.
Air Conditioning: Heat exchangers are too utilized in automotive air conditioning frameworks to transfer heat from the refrigerant to the exterior air, keeping the cabin cool.
4.2 Aviation and Marine
Aircraft Systems: In aviation, heat exchangers oversee the temperature of basic systems, such as motors and pressure driven systems, ensuring safe and productive operation at tall altitudes.
Marine Applications: In ships, heat exchangers are utilized to cool engines, decrease exhaust emissions, and give heating and cooling for onboard systems.
5. Environmental Sustainability
5.1 Waste Heat Recuperation
Industrial Forms: Heat exchangers are utilized in waste heat recuperation systems to capture and reuse heat from industrial forms, diminishing energy utilization and greenhouse gas emissions.
Power Plants: In power plants, heat exchangers recover waste heat from debilitate gases or steam, utilizing it to preheat approaching feedwater or produce extra power, in this manner improving generally efficiency.
5.2 Renewable Energy Integration
Heat Pumps: Heat exchangers are basic components of heat pumps, which extract heat from the air, ground, or water to supply proficient heating and cooling in buildings, essentially diminishing reliance on fossil fuels.
Conclusion
Heat exchangers are the unsung heroes of modern innovation, playing a imperative part in controlling our world. By empowering productive heat exchange in power generation, industrial forms, HVAC systems, transportation, and natural supportability, heat exchangers contribute to vitality proficiency, taken a toll savings, and diminished environmental impact. As the world proceeds to move towards more economical vitality arrangements, the significance of heat exchangers in driving this change will as it were grow, making them crucial to the future of energy and innovation.