Indoor Agriculture and Vertical Farms
Introduction
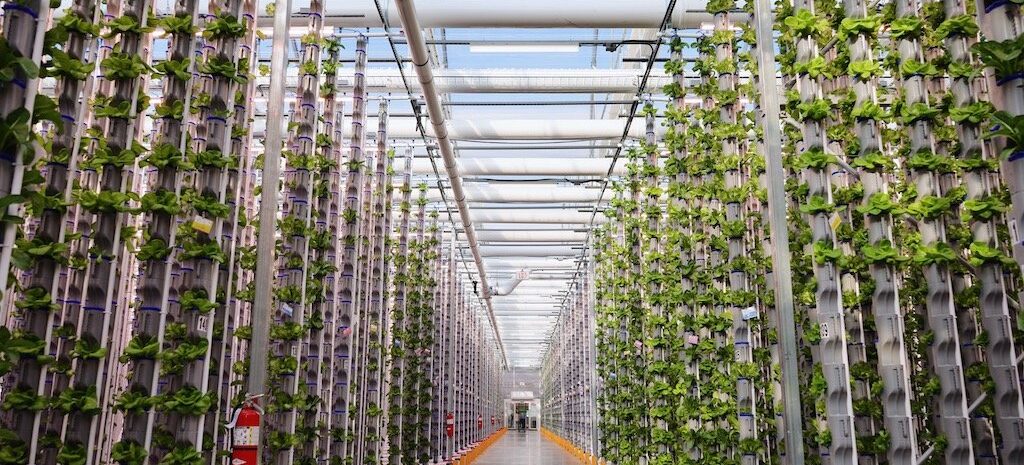
Indoor Agriculture and Vertical Farms are revolutionizing how we grow crops, offering year-round cultivation in controlled environments. However, managing temperature and humidity levels is crucial to ensure optimal crop growth. Innovations in cooling systems for indoor agriculture are driving efficiency and sustainability in these growing environments. By integrating advanced technologies such as precision climate control, water-cooled systems, and energy-efficient chillers, modern cooling systems enable vertical farms to thrive even in dense urban settings.
Key Innovations:
- Hybrid Cooling Systems
A combination of air-cooled and water-cooled systems, hybrid cooling technologies balance energy efficiency and water usage. These systems automatically switch between cooling methods based on ambient conditions and cooling needs, optimizing resource use while maintaining consistent temperatures for crops. - Phase Change Materials (PCMs) in Cooling
Phase change materials can store and release thermal energy as they change between solid and liquid states. By incorporating PCMs into cooling systems, vertical farms can achieve better temperature regulation and reduce energy consumption, especially during peak demand periods. - Zoning and Microclimates
Innovations in cooling systems allow vertical farms to create specific zones or microclimates within the same facility. This zoning capability enables farmers to grow different crops with distinct cooling needs in close proximity, maximizing space usage and crop diversity. - Smart Ventilation Systems
Intelligent ventilation systems are integrated with sensors to monitor air quality and temperature in real time. These systems can automatically adjust airflow to maintain the ideal conditions, reducing the risk of overheating and enhancing air circulation, which is vital for plant health. - Low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) Refrigerants
The development and adoption of refrigerants with low global warming potential are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of cooling systems in vertical farms. These refrigerants not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also enhance energy efficiency. - Remote Monitoring and Automation
Cloud-based platforms enable farmers to monitor cooling systems remotely, adjusting settings in real-time from any location. Automated controls powered by AI further reduce the need for manual intervention, ensuring that the cooling system responds to changing conditions instantly, improving reliability. - Humidity Control in Conjunction with Cooling
Modern cooling systems are equipped with advanced humidity control mechanisms that work in conjunction with temperature regulation. This helps prevent excessive moisture buildup, which can lead to fungal infections and other crop diseases, ensuring healthier plants. - Vertical Space Optimization through Cooling Distribution
Innovative cooling designs are being adapted to fit the vertical architecture of these farms. Cooling systems are positioned strategically to distribute cold air efficiently across multiple layers of plants, ensuring uniform cooling from top to bottom. - Energy Management and Demand Response Systems
Smart cooling systems are integrated with energy management platforms, allowing vertical farms to participate in demand response programs. By reducing energy usage during peak grid demand, these systems help lower operational costs while contributing to grid stability. - Water Reuse in Cooling Systems
Some advanced cooling systems in vertical farms recycle water used for cooling and direct it back into irrigation systems, promoting water conservation. This closed-loop system reduces water waste and increases sustainability in water-scarce environments. - Cooling Solutions for High-Density Lighting Systems
High-density LED lighting in vertical farms generates substantial heat. Advanced cooling systems are designed to dissipate this heat efficiently, maintaining optimal temperatures while minimizing energy consumption. Indoor Agriculture and Vertical Farms - Advanced Insulation and Sealing for Heat Retention
Efficient insulation in walls, ceilings, and doors ensures that less energy is wasted on cooling. By minimizing heat ingress, advanced insulation helps cooling systems work more efficiently, reducing energy costs for indoor agriculture operations.