Oil and Gas Heat Exchanger
Introduction
Oil and Gas Heat Exchanger is one of the most energy-intensive sectors, requiring advanced thermal management solutions to ensure efficient operations, cost savings, and process reliability. Heat exchangers play a critical role in facilitating the transfer of heat between process fluids, which is essential for various applications such as crude oil refining, gas processing, power generation, and petrochemical production. These heat exchangers are used for cooling, heating, condensing, and recovering heat energy, making them indispensable in both upstream and downstream processes. Given the extreme operating conditions in the oil and gas industry—such as high pressures, elevated temperatures, and exposure to corrosive substances—selecting the right heat exchanger is crucial. Engineers must consider factors such as fluid properties, temperature differentials, heat transfer efficiency, space constraints, and maintenance requirements. The right heat exchanger not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances safety, environmental compliance, and energy conservation. With growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, modern heat exchangers are designed to optimize thermal performance while minimizing environmental impact.
Types of Heat Exchangers Used in Oil and Gas Industry
Various types of heat exchangers are used in the oil and gas sector, each designed to handle specific operational challenges. Here are the most common types:
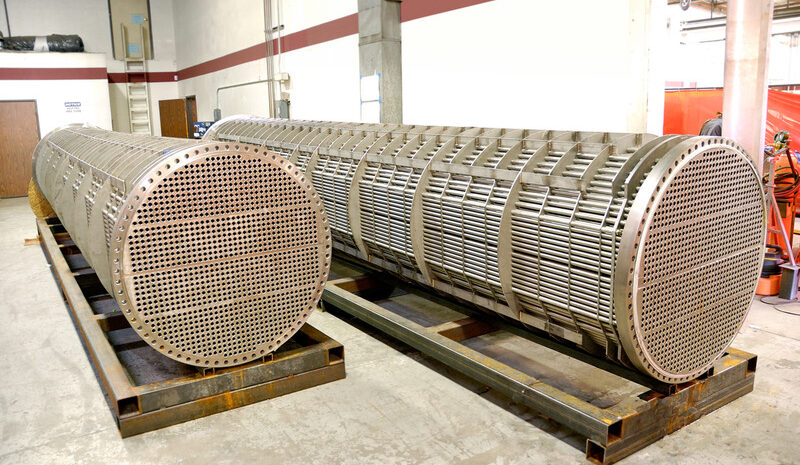
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
- One of the most widely used types in the oil and gas sector due to its high-pressure and high-temperature handling capability.
- Consists of a bundle of tubes enclosed within a shell, where one fluid flows through the tubes while another flows around them.
- Commonly used for crude oil refining, natural gas processing, and cooling lubricating oils in turbines and compressors.
- Known for durability, easy maintenance, and the ability to handle dirty or viscous fluids.
- Can be customized with different tube materials to withstand corrosion and fouling.
Plate Heat Exchangers (PHEs)
- Highly efficient heat exchangers with compact designs.
- Uses thin metal plates with gaskets to create multiple heat exchange channels.
- Suitable for low to medium pressure applications, such as LNG regasification, gas dehydration, and oil cooling.
- Offers high thermal efficiency, making them ideal for recovering heat in energy-intensive operations.
- Easier to clean and maintain compared to shell and tube heat exchangers.
Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers (ACHEs)
- Used in oil and gas fields, refineries, and offshore platforms where water resources are limited.
- Instead of water, these exchangers use forced air to cool down process fluids.
- Essential for cooling natural gas, compressed air, and process vapors in areas with harsh environmental conditions.
- Lower operational and maintenance costs, reducing the need for water treatment.
Fin-Fan Heat Exchangers
- A type of air-cooled heat exchanger, mainly used in gas compression stations and petrochemical plants.
- Features extended finned tubes that increase heat transfer efficiency.
- Provides effective cooling for various hydrocarbon processes and compressor discharge gases.
Spiral Heat Exchangers
- Consists of two concentric spiral channels, allowing efficient counterflow heat exchange.
- Used in applications where fouling is a concern, such as heavy oil processing, bitumen cooling, and sludge heat recovery.
- Designed for handling high-viscosity fluids and slurries, reducing the risk of clogging and scaling.
Welded Plate Heat Exchangers (WPHEs)
- Similar to traditional plate heat exchangers but with welded plates instead of gaskets.
- Used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications in oil and gas refining.
- Can handle aggressive fluids and corrosive gases without risk of gasket failure.
Key Applications of Heat Exchangers in the Oil and Gas Industry
Heat exchangers serve multiple critical functions in various oil and gas processes, including:
Crude Oil Preheating
- Heat exchangers are used to preheat crude oil before it enters the distillation column in refineries.
- Increases separation efficiency and reduces energy consumption in the refining process.
Cooling of Lubricating Oils
- Essential for gas turbines, compressors, and pumps in oil and gas plants.
- Prevents overheating and breakdown of critical machinery.
Natural Gas Processing
- Used in gas dehydration, liquefaction (LNG), and cryogenic separation processes.
- Enables efficient removal of moisture, CO₂, and other impurities from natural gas.
Heat Recovery Systems
- Recovers heat from flue gases, steam condensers, and process waste heat.
- Improves energy efficiency and sustainability in refineries and petrochemical plants.
Sulfur Recovery and Hydrogen Processing
- Heat exchangers play a key role in hydrotreating and hydrocracking processes.
- Used for cooling sulfur recovery units and hydrogen gas streams.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Heat Exchanger
Choosing the right heat exchanger requires careful consideration of various factors:
- Operating Temperature and Pressure – Must withstand extreme high-temperature and high-pressure conditions in refining and gas processing.
- Material Selection – Should be resistant to corrosive hydrocarbons, sulfur compounds, and high-salinity fluids. Common materials include stainless steel, titanium, and exotic alloys.
- Heat Transfer Efficiency – High-efficiency exchangers reduce fuel consumption and improve operational savings.
- Footprint and Installation Space – Compact options like plate heat exchangers are preferred in space-constrained environments.
- Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements – Some exchangers, like shell and tube heat exchangers, allow mechanical cleaning, while others require chemical cleaning methods.
- Fouling Resistance – Critical in handling heavy oils, waxes, and sludge, reducing downtime and cleaning costs.
Advantages of Using Heat Exchangers in Oil and Gas Industry
Enhances energy efficiency by reducing waste heat loss.
Improves safety by maintaining optimal temperatures in critical processes.
Extends equipment lifespan by preventing overheating and excessive wear.
Reduces operational costs by optimizing fuel consumption and process efficiency.
Enables sustainable operations by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and improving heat recovery.
Conclusion
Oil and Gas Heat Exchanger ensuring optimal thermal energy transfer, process efficiency, and equipment longevity. They support a wide range of applications, from crude oil preheating and gas dehydration to heat recovery and compressor cooling. The selection of the right heat exchanger is essential for maintaining operational safety, reducing downtime, and optimizing energy consumption in both onshore and offshore facilities. As the industry moves toward greater efficiency and sustainability, advancements in heat exchanger materials, designs, and maintenance strategies continue to shape the future of thermal management. By investing in high-performance heat exchangers, oil and gas companies can achieve better energy utilization, lower operational costs, and improved environmental responsibility. Ultimately, heat exchangers serve as a key enabler of energy optimization in oil and gas operations, ensuring continuous production, reduced emissions, and long-term cost savings. Choosing the right solution tailored to specific process requirements will help companies stay competitive in an evolving energy landscape.